Various Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis Worth Knowing
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that occurs when a blood clot blocks the vein located deep inside your body. A blood clot is a lump of blood that is solid, however jelly-like. The blood clots that reside deep inside the veins especially in the thigh or the lower leg are more harmful. However, they can also develop in other parts of the body. Some other names for this condition are thromboembolism, post-phlebitic syndrome or post-thrombotic syndrome.
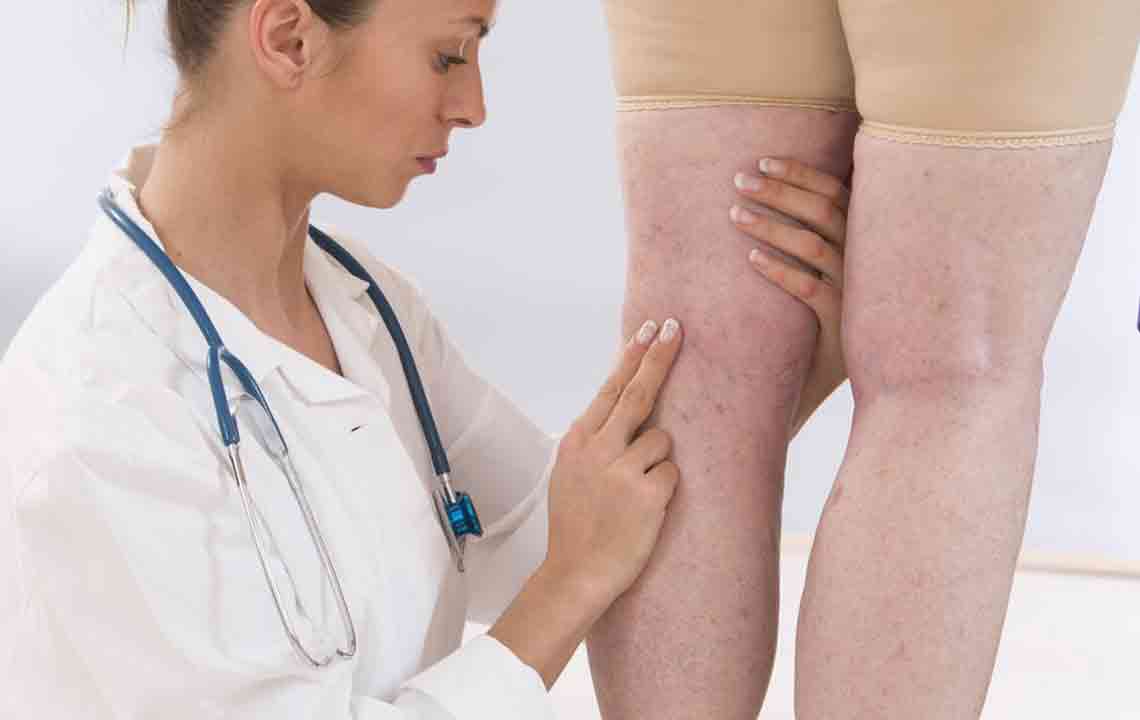
The symptoms of deep vein thrombosis are many. However, it occurs usually in people who are over fifty years of age. A lot of times, it depends on what your body’s blood flow is like. Some of the underlying causes of DVT have been listed below.
- Previous injury that caused vein damage.
- Being overweight since that puts a lot of pressure on your veins.
- Having a DVT family history.
- Undergoing hormone therapy or contraceptives.
- Smoking regularly.
- Staying seated in one position for a very long time.
- Having a catheter placed in one of the veins.
The signs and symptoms of deep vein thrombosis might be related to pulmonary embolism. If that is the case, go see your doctor immediately. Both of these conditions may become problematic if not treated in time.These are usually seen in legs that are affected by the deep vein clot. Only about half the people suffering from deep vein thrombosis have symptoms that are noticeable.Common symptoms of deep vein thrombosis have been listed below.
- Swelling of a vein inside or along the leg.
- Sensitivity or tenderness in the leg that is mainly felt when you are either walking or standing.
- Extreme warmth or heat felt around the area that is affected.
- Discolored or red skin on the leg.
- A lot of people are not aware of the clot deep inside their vein until and unless they see signs of a pulmonary embolism. These include:
- Inexplicable shortness of breath
- Trouble with deep breathing
- Coughing up blood
- Rapid breathing
- Fast heart rate
Similarly, in some cases, there might be no symptoms of deep vein thrombosis. If in case these symptoms do occur, you may experience one or more of the following symptoms.
- A very heavy shooting pain in the affected area, which occurs in intervals or could even, be continuous at times.
Redness on the back of the leg - Extreme sensitivity to touch
Deep vein thrombosis and its symptoms and signs usually affect only one of the legs. The pain may get worse as and when you bend your knee or foot. If it is left untreated, one out of every ten people are likely to develop pulmonary embolism. It is a very serious condition that acts as a symptom for deep vein thrombosis and causes breathlessness, pain in the chest, sudden fainting or collapsing. All of these conditions require immediate medical attention. If you develop symptoms of deep vein thrombosis, you should consult your doctor. In case you develop pulmonary embolism because of the same, you need to see the doctor immediately. Some people may not be able to realize that they are showing symptoms of deep vein thrombosis until they have ended up in the emergency room for a pulmonary embolism. Sometimes, the arteries become so blocked that it is hard for the doctor to take out the clots without harming the walls surrounding it.
To diagnose whether or not you have DVT, your specialist or doctor will first conduct a general health test that will include your medical history and the symptoms. Then a physical examination will be conducted. Also, since symptoms of deep vein thrombosis are shared by many other diseases and problems, one might need to go through specific kind of tests. This can help your doctor rule out other problems and confirm a specific diagnosis.
If you reach a stage where you start having pulmonary embolisms, it is possible that you have or will cause serious damage to your lungs and even other body parts. The symptoms that will warn you whether you are about to have an attack are the ones listed below.
- Dizziness or black outs
- Sweating or anxiety
- Chest pain that gets worse with coughing or inhaling deeply
- Breathing heavily
- Coughing up blood
- Increased heart rate
When it comes to treating the problem, you might have to get filters put inside the vena cava, an abdominal vein in case the blood thinners do not work. This treatment helps in getting rid of the pulmonary embolisms as it stops these clots from entering the lungs.
Your doctor might even prescribe you with some medications that can help in thinning your blood clots. These include warfarin and heparin. These make it difficult for the blood to clot in the veins. Moreover, it helps in shrinking or dissolving the clots that are already present and minimizes the chance for you to develop any further clots.